Introduction
As websites grow and traffic patterns become unpredictable, traditional hosting models often struggle to keep up. Sudden traffic spikes can slow down servers, and single-server failures can cause downtime. This is where cloud hosting becomes relevant.
Cloud hosting is designed to offer high reliability, scalability, and performance by distributing websites across multiple servers instead of relying on a single machine.
This article explains what cloud hosting is, how cloud hosting works, its benefits and limitations, and who should choose cloud hosting. It also helps you understand when cloud hosting is a better choice than VPS or shared hosting.
This article is part of our complete web hosting and domain guide (pillar page), which covers hosting fundamentals, types, performance, and SEO impact in detail.
What Is Cloud Hosting?



Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting where a website runs on a network of interconnected servers, commonly referred to as the “cloud,” rather than a single physical server.
Instead of storing all website data on one machine, cloud hosting distributes data and workloads across multiple servers. These servers work together to deliver website content quickly and reliably.
In simple terms, cloud hosting removes the dependency on one server and spreads the load across many servers.
How Cloud Hosting Works
In cloud hosting, your website is hosted on a cluster of servers connected through a centralized system. These servers share resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage.
When a user visits your website, the request is handled by the most available or best-performing server in the network. If one server becomes overloaded or fails, another server immediately takes over.
This architecture ensures high availability and minimizes downtime, even during heavy traffic or hardware failures.
Why Cloud Hosting Is Different from Traditional Hosting
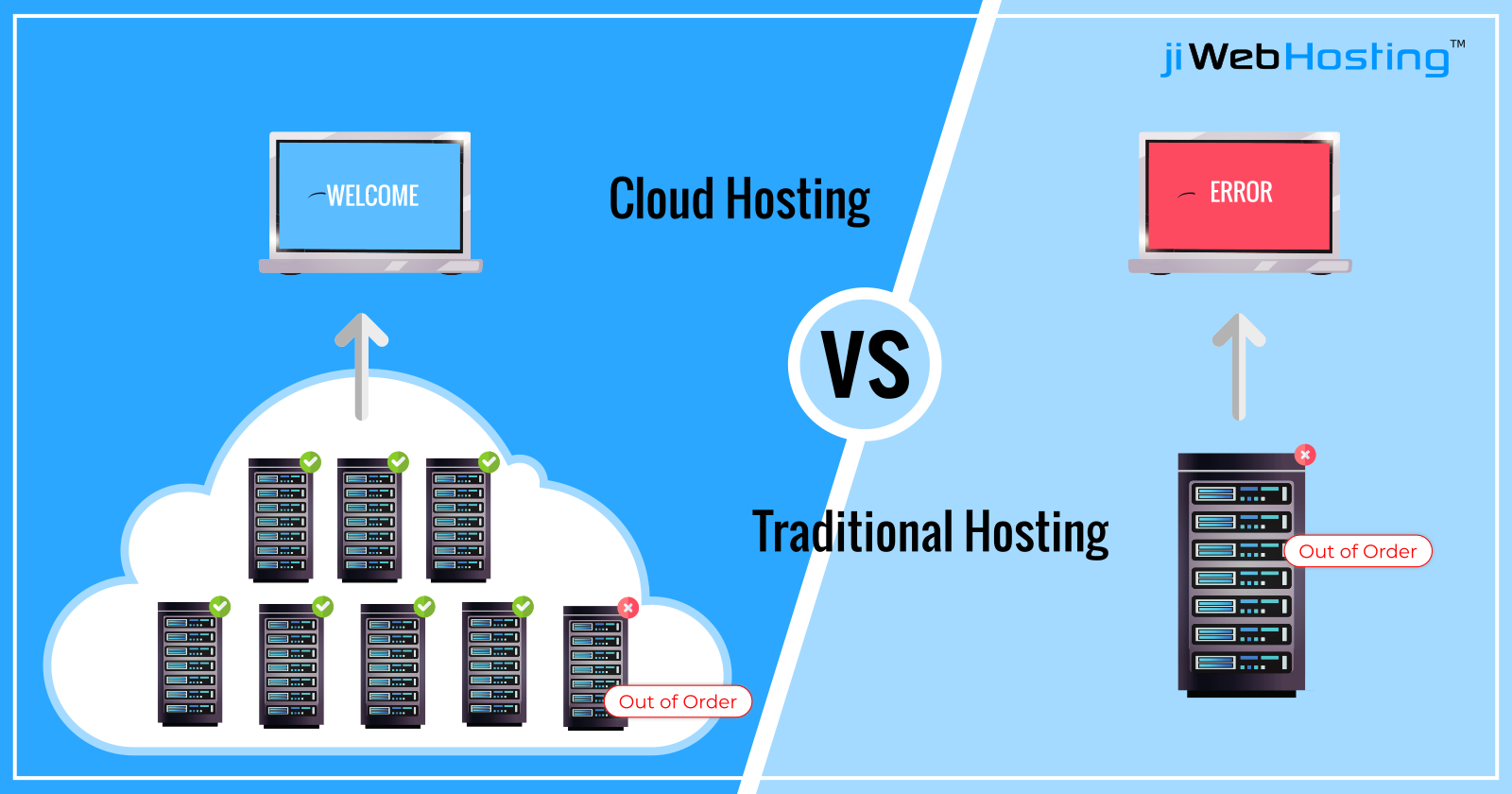

Traditional hosting models such as shared or VPS hosting rely on a single physical server. If that server faces issues, websites hosted on it are affected.
Cloud hosting removes this single point of failure. Since multiple servers are involved, websites remain online even if individual servers encounter problems.
This difference makes cloud hosting more resilient and scalable compared to traditional hosting options.
Key Benefits of Cloud Hosting
One of the biggest advantages of cloud hosting is scalability. Resources can be increased or decreased dynamically based on traffic needs. This is especially useful for websites that experience sudden or seasonal traffic spikes.
Cloud hosting also offers high uptime. Since websites are not tied to one server, downtime is significantly reduced.
Performance is another major benefit. Load balancing ensures that no single server becomes overloaded, resulting in faster page load times and better user experience.
For businesses, cloud hosting provides flexibility. Websites can scale without complex migrations or downtime.
Limitations of Cloud Hosting



Despite its advantages, cloud hosting has some limitations.
Cost management can be challenging. Many cloud hosting plans use usage-based pricing, which means costs can increase as resource usage grows. Without proper monitoring, expenses may rise unexpectedly.
Cloud hosting can also be more complex than shared hosting. While many providers offer managed solutions, the underlying architecture is more advanced.
For very small websites with stable, low traffic, cloud hosting may be unnecessary and cost-inefficient.
Cloud Hosting vs VPS Hosting: Understanding the Difference
VPS hosting provides dedicated resources on a single physical server, offering stability and predictable pricing.
Cloud hosting distributes resources across multiple servers, offering higher reliability and scalability.
VPS hosting is ideal for steady, predictable traffic. Cloud hosting is better for websites with fluctuating or rapidly growing traffic.
The choice depends on how your traffic behaves rather than which option sounds more advanced.
Is Cloud Hosting Good for SEO?
Cloud hosting can positively support SEO by improving website speed, uptime, and reliability.
Faster page loads and fewer outages improve user experience, which indirectly benefits search performance. Cloud hosting also handles traffic spikes better, preventing slowdowns during high-demand periods.
However, cloud hosting alone does not guarantee better rankings. It provides the infrastructure needed to support SEO efforts, but content quality and optimization remain essential.
For deeper insights, refer to our guide on how hosting affects website speed and best server location for Indian websites.
Who Should Use Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is ideal for websites that require flexibility and reliability.
It works well for eCommerce websites, SaaS platforms, content publishers with high traffic, and businesses running marketing campaigns that cause traffic spikes.
Startups planning rapid growth also benefit from cloud hosting because it supports scaling without major infrastructure changes.
When Should You Upgrade to Cloud Hosting?
Upgrading to cloud hosting makes sense when VPS hosting can no longer handle traffic variability or uptime requirements.
If your website experiences sudden traffic surges, downtime during peak periods, or frequent resource bottlenecks, cloud hosting is often the best solution.
Planning this upgrade early helps avoid performance issues that can affect SEO, conversions, and user trust.
Cloud Hosting and Website Performance
Cloud hosting architecture improves performance by distributing load across multiple servers. This reduces server response times and improves stability under heavy traffic.
Load balancing, redundancy, and dynamic resource allocation make cloud hosting one of the most performance-oriented hosting solutions available today.
To understand performance in more detail, read our dedicated guide on how hosting affects website speed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is cloud hosting in simple words?
Cloud hosting means your website runs on multiple connected servers instead of one server.
Is cloud hosting better than VPS hosting?
Cloud hosting offers better scalability and uptime, while VPS hosting offers predictable pricing and control.
Is cloud hosting expensive?
Cloud hosting can be cost-effective, but usage-based pricing requires monitoring to avoid unexpected costs.
Is cloud hosting suitable for beginners?
Managed cloud hosting can be suitable for beginners, but shared hosting is often simpler for very small websites.














